Study from Shanxi University published in top chemistry journal
Updated: 2020-10-09
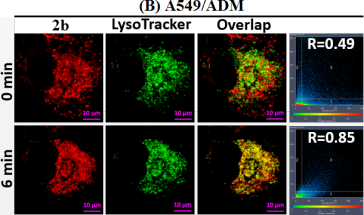
A diagram in the research article from Shanxi University that is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. The first author of the article is Zhang Hongxing, a teacher from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at the university and a member of the research team led by Guo Wei, a professor at the school. [Photo/sxu.edu.cn]
Researchers from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Shanxi University recently published their findings in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, a preeminent global journal that focuses on chemistry and interfacing areas of science.
The research paper, entitled Carbon-Dipyrromethenes (Cardipys for short): Bright Cationic Fluorescent Dyes and Potential Application in Revealing Cellular Trafficking of Mitochondrial Glutathione Conjugates, showcases that the new Cardipys positive ion fluorescent dye developed by the research team can reveal the intracellular detoxification mechanism of mitochondrial toxic electrophiles.
The Cardipys developed by the team retain the excellent photophysical properties of conventional boron–dipyrromethenes and demonstrate improved water solubility and photostability. They provide an excellent imaging tool for the study of mitochondrial function due to their positive ion characteristics.
The research article also shows that these Cardipys are likely to have great potential in exploring the drug resistance of cancer cells and screening more effective anticancer drugs.
INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION EXCHANGE
-
 Confucius Institutes
Confucius Institutes The Confucius Institutes are set up worldwide by the Chinese Language Council International to promote Chinese language and culture.
-
 Enrollment of Foreign Students in Shanxi University
Enrollment of Foreign Students in Shanxi University Join us and explore our wide range of study programs and enjoy a first class educational experience that makes you a part of a lively global community.

