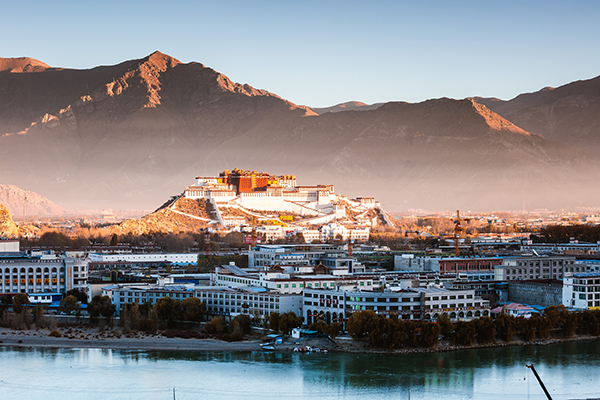
Ecological progress on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Updated: 2018-07-19  Print
Print 

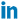

Researchers collect plant samples at Mount Gongga in Sichuan province, on Nov 26. The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, which also covers parts of Sichuan, is a key eco-safety barrier in China and Asia, and a focus of the country's drive to promote ecological progress. JIN LIWANG/XINHUA
III. Steady Improvement of Environmental Quality
The central and local governments have carried out a number of environmental protection projects for comprehensive improvement of river basins, improvement of urban and rural living conditions, and prevention and control of pollution from factories and mines. As a result, the environmental quality and living conditions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau have steadily improved.
Quality of the water environment has kept improving.
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is where a number of Asia's largest rivers see their headwaters; it is one of the regions under the strictest water resource management and water environment protection in China.
The State has reinforced protection on the Plateau with a set of key measures including: Compiling comprehensive planning for major water bodies, demarcating the functional zones of rivers and lakes, clearly defining the functions of water bodies and the goals of water quality protection, determining the pollution accommodating capacity of major rivers and lakes and the total volume of discharges allowed, and introducing a strictest system of water resource management.
A system of assessment quotas has been established at three administrative levels-province (autonomous region), prefecture (city) and county (district)-as a measure to promote water environment protection and restoration and ensure the security of water ecology on the Plateau.
During the 12th Five-year Plan period, the state spent RMB25.31 billion on Plateau projects related to rural drinking water, water and soil conservation, and water conservation on pasture land, providing safe drinking water to 4.57 million farmers and herdsmen, and building water supply facilities for 1,400 monasteries.
Drinking water is now safe in areas where local water has high fluoride and arsenide levels, tastes bitter and salty or is highly polluted, and in places that are seriously short of water. In 2014, the state invested RMB478 million in the environmental improvement and ecological restoration projects of Namco, Yamzho Yumco, Keluke Lake and the lakes at the source of the Yellow River.
In recent years, a total of 1,730 sq km of land have been saved from soil erosion due to the effort invested in small river basin ecological improvement and hillside land soil conservation. Thanks to the ecological protection endeavors at the source of three large rivers, the Qinghai Lake and the Qilian Mountains, 60 billion cu m of quality water is supplied to downstream areas every year.
At present, the major rivers and lakes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are basically in their original natural conditions with good water quality.
Soil functions have been effectively enhanced.
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is one of the least polluted areas on earth, and the soil environment is overall in its original environmental background state. The soil types and the heavy metal element content are determined by the property of parent rocks and climatic conditions, and little impacted by human activities.
The content of copper, nickel, lead and other heavy metals in the local lake deposits is lower than those of lake deposits in places more frequented by humans. The heavy metal content in the arable soils is lower than the national standards for soil of Grade I.
Along with the implementation of ecological and environmental protection measures, the ecological functions of the local soils have been effectively enhanced. Over the last 50 years, the carbon storage in China's grassland soils has displayed a tendency of undulating increase, with the grasslands on the Plateau contributing the most (63.1 percent) and the inorganic carbon pool in the soils three meters under the alpine grasslands accounting for 70 percent of the national total.
The annual water conservation volume is 345 billion cubic meters. Following the completion of phase I of the Sanjiangyuan ecological protection and construction project, the annual water conservation volume of the forest and grassland ecosystems has increased by 15.6 percent, and fencing the forests has also contributed to improvement in the organic carbon, moisture and micro-organics content in the soils.
Air environment has maintained good quality.
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has a low intensity of human activity. The air quality is little impacted, the types of pollutants are few and the density is low, and the content of pollutants is similar to those at the North Pole. With the promotion of use of green energy, the progress in building ecological towns, and efforts to improve rural environment, the air quality on the Plateau has seen further improvement. Of the 96 key cities whose annual density of particles met relevant standards in 2016, 16 were located on the Plateau. The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is still one of the cleanest regions on earth.
Living environment has notably improved.
The state has spent some RMB6.3 billion since 2009 on domestic sewage and waste disposal projects and sewage conduits in the towns of Tibet autonomous region, Qinghai province and the Tibetan-inhabited towns in Sichuan, Yunnan, and Gansu provinces, leading to a significant increase in local disposal capacity. Since the 12th Five-year Plan period, the state has invested RMB5.45 billion improving the rural environment on the Plateau. Of this sum, RMB349 million went to Tibet, 1.63 billion to Sichuan, 1.45 billion to Yunnan, 899 million to Gansu, and 1.12 billion to Qinghai.
The Tibet autonomous region has worked to improve the living conditions of urban and rural communities and address problems related to garbage classification, noise pollution, sewage discharge, and straw burning.
Since 2010, it has allocated RMB11.82 billion for the improvement of living conditions in more than 5,261 villages, and introduced long-term mechanisms for rural environment management and protection.
Since 2008, Qinghai province has allocated RMB1.74 billion of special funds for the environmental improvement of over 3,015 villages and settlements of nomadic people, benefiting 2.2 million people-76 percent of its rural population.
In 2014, Qinghai started a beautiful village project, in which it had invested RMB10.77 billion by the end of 2017.
Today, the rate of urban domestic sewage disposal has reached 78 percent and domestic waste bio-safety disposal 96.69 percent, and the living conditions have been notably improved in cities and towns. The Garze prefecture of Sichuan province has carried out a three-year action to address waste and sewage problems, and directed RMB275 million of local government special bond funds into new urbanization efforts.
By the end of 2017, the Aba prefecture of Sichuan province had invested RMB585 million in sewage and waste disposal facilities. The Deqen prefecture of Yunnan province has prohibited the sale, supply and usage of non-degradable plastic products in the areas under its jurisdiction, and achieved marked progress in water, soil and air pollution control. The Gannan prefecture of Gansu province has spent RMB5.25 billion creating 703 "well-off villages" with a pleasant ecological environment, ending up in improving their infrastructure, public services, and social security.
IV. Steady Development of Green Industry
With the goal of protecting the fragile ecological environment, the provinces and autonomous regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau work hard to control the intensity of resource exploitation and utilization. Efforts are made to maintain a good environment and a high degree of public satisfaction with ecological progress, and to achieve green development. An economic model featuring a circular economy, renewable energy, and distinctive industries, is forming on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, signaling an increasing level of green development.
Green production has begun to take shape.
In their efforts to create a green development model, provinces and autonomous regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are committed to an eco-friendly path to economic growth involving low and intensive utilization of resources.
The State has established two national circular economy pilot industrial parks in Qinghai province-Qaidam Circular Economy Pilot Area and Xining Economic and Technological Development Zone. Industrial activities in Qaidam Circular Economy Pilot Area include salt lake chemical, oil and gas chemical, metallurgy, comprehensive utilization of coal, new energy, new materials and special biological industries, with more intensive utilization of the local resources.
Xining Economic and Technological Development Zone features nonferrous metals, chemicals, alpine biological products, traditional Chinese medicine (including Tibetan medicine), Tibetan carpets, playing a leading and exemplary role in improving the quality and increasing the benefits of development. A basic green industry framework is now in place, extending the industrial chain and improving the infrastructure.
Based on its resource strengths, the Tibet autonomous region has been endeavoring to optimize and upgrade its industrial structure. It has worked out the Circular Economy Development Plan of the Tibet autonomous region (2013-2020).
Efforts are focused on clean energy, tourism, culture, characteristic foods, natural drinking water, transport, commerce, logistics, finance, information services, and other green low-carbon economic activities. In 2016 Lhasa was designated as a national demonstration city for the circular economy, and is now working in accordance with the Establishing the Implementation Plan of Circular Economy Demonstration City for Lhasa of the Tibet autonomous region.
Relying on its resource strengths, Yunnan province's Deqen prefecture is focusing on four major sectors (foods, drugs, beverages and ornamental products) and on the construction of green industrial parks, along with a burgeoning biological industry. In accordance with the ecological functions of local areas, Gansu province's Gannan prefecture has developed a strategy of "building an eco-friendly prefecture", and defined the future direction of green industry.
Unique strengths of local agriculture and animal husbandry have become increasingly outstanding.
Provinces and autonomous regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau focus on unique agriculture and animal husbandry, cultivating green and organic agricultural and livestock products and brands, and building pilot areas for ecological agriculture and animal husbandry. These have become an important part of the green economy on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
Since 2004, the state has invested more than RMB3 billion in Tibet, directed to more than 450 projects in 10 categories related to agriculture and animal husbandry unique to the region, including highland barley, yak-breeding, and traditional Tibetan medicine. More than 100 leading enterprises have emerged as a result, increasing the incomes of local farmers and herdsmen by RMB1.18 billion and benefiting 1.75 million people.
The Tibet autonomous region is pressing forward with the certification of products of specified geographical origin, developing unique brands, and speeding up development of animal husbandry and agricultural products. To date, more than 10 farm and pastoral products of specified geographical origin have been certified by relevant government departments, including Pagri yak, Gamba sheep, Lhünze black highland barley, Zayu kiwi fruit and Bome Gastrodiaelata.
Qinghai province focuses on four industries, i.e., grain and oil crop, livestock and poultry, fruit and vegetable, and Chinese wolfberry and sea buckthorn. Each of these represents output value of more than RMB10 billion.
The speed of optimization of a ternary structure of grain, cash and forage crops is picking up. The building of national grassland ecological animal husbandry pilot areas, modern agriculture demonstration zones and industrial parks are making headway. By the end of the 12th Five-year Plan, there were 1,879 family farms and pastures, 8,876 cooperatives of various types, and 451 leading agriculture and animal husbandry enterprises in Qinghai.
Crops unique to the region represented 85 percent of planting by area, and the coverage rate of improved varieties of crops was 96 percent. The corresponding figures for improved breeds of livestock & poultry and aquatic products were 62 percent and 95 percent.
The total annual output of eco-friendly green and organic agricultural and livestock products reached 1.09 million tons. An agricultural products quality traceability system has been implemented.
A "three areas and one zone" development framework for agriculture and animal husbandry is in place; this refers to a characteristic planting and high efficiency demonstration area in the east, a circular economic development pilot area in a farming-pastoral ecotone area around the lake, an ecological and organic animal husbandry protection and development area in southern Qinghai, and a cold water moderate aquaculture development zone along the Yellow River.
In order to accelerate the development of its growing industry unique to the region, forest and fruit industries, and the industry of byproducts of forests, Gansu province's Gannan prefecture focuses on the building of a highland barley base and barley industrialization project in the Tibetan-inhabited area, construction of the bases of highland quality rape and traditional Chinese medicine (including Tibetan medicine).
Sichuan province's Garze prefecture and Aba prefecture integrate ecological progress with ecological agriculture, construct bases for characteristic agriculture and animal husbandry and the forest and fruit industries each covering a total area of more than 100 million mu (133,400 hectares), and develop planting bases for Chinese prickly ash, forest vegetables, and woody herbs.
In 2017, the area for growing crops unique to the locality in Yunnan province's Deqen Prefecture reached 90,700 hectares, turning out an output value of RMB1.9 billion.
Green energy develops rapidly.
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is rich in hydro energy, solar energy, geothermal energy, and other green energies. In recent years, the provinces and autonomous regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau have each built its own basic renewable energy industry system focusing on hydroelectricity and solar energy to support the coordinated development of the regional economy and environmental protection.
On the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, many big rivers, running through high mountains and canyons, boast significant potential for hydropower development.
Tibet leads the country with 174 million kW of potential hydropower. In recent years, Tibet has built three medium-scale hydropower stations, i.e., Duobu, Jinhe and Drigung. By the end of 2017, Tibet's installed hydropower capacity was 1.77 million kW, accounting for 56.54 percent of the region's total installed capacity.
With 24 million kW of exploitable hydropower resources, Qinghai province has built three large hydropower projects, i.e., Longyang Gorge, Laxiwa, and Lijia Gorge. By the end of 2016, Qinghai's installed hydropower capacity was 11.92 million kW.
Sichuan province's Garze prefecture and Aba prefecture boast 56.63 million kW of exploitable hydropower, and 17.08 million kW of installed capacity in completed hydropower stations.
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau area is a world-leading source of solar energy, with 5,400-8,000MJ per sq m of annual total solar radiation, 50-100 percent higher than low-elevation areas on the same latitude.
Qinghai province has launched several photovoltaic (PV) power station projects in the Qaidam Basin, each with a capacity of at least one million kW, and is planning to build the world's largest PV power station. By the end of 2016, Qinghai's installed PV capacity had reached 6.82 million kW.
In 2014, Tibet received approval from the state to develop PV power stations without limit in scale of construction and enjoying priority state support. By the end of 2017, Tibet's installed PV capacity was 790,000 kW.
Sichuan province's Garze Prefecture and Aba Prefecture have more than 20 million kW of exploitable solar energy, and PV power stations with a total capacity of 350,000 kW are in service.
Tourism boosts green development.
The unique natural and cultural landscape on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau provides rich potential for tourism, encouraging the catering, accommodation, transport, culture, and entertainment sectors, and protecting cultural heritage and the survival of traditional crafts, and the development of characteristic products. Tourism has become an important channel for green growth and higher incomes for farmers and herdsmen.
Giving top priority to ecological protection, provinces and autonomous regions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are promoting characteristic and holistic tourism, building new tourism infrastructure and supporting facilities, and encouraging tourism to integrate with the cultural, sports and health industries.
The Tibet autonomous region is developing ecological tourism and quality holistic tourist routes based on nature reserves, national forest parks, and national wetland parks. Sichuan province focuses on developing the Jiuzhaigou-Ruoergai Grassland tourism economic circle, and holistic tourism demonstration areas in Aba Prefecture and Garze Prefecture.
Gansu province is cultivating landscape and prairie and wetland eco-tours, building garbage-free demonstration areas for holistic tourism in Gannan Prefecture, and coordinating growth in tourism with eco-environmental protection.
In 2017, Tibet hosted more than 25.61 million visitors and its revenues totaled RMB37.94 billion, representing 28.95 percent of the region's GDP; Qinghai received 34.84 million visitors and its revenues totaled RMB38.15 billion, representing 14.44 percent of the province's GDP. In 2017, Yunnan province's Deqen prefecture received 26.76 million visitors, providing revenues of RMB29.8 billion. The number of visitors to and the tourism revenues of the plateau region of Gansu province have grown at a double-digit rate for the last seven years. In 2017, it received 11.06 million tourists providing revenues of more than RMB5.14 billion.








