Remarkable Results in Ethnic and Religious Work
Updated: 2021-05-21 (Xinhua)  Print
Print 

The state formulates guidelines and policies to fully implement the system of regional ethnic autonomy, protect normal religious activities in accordance with the law, and promote the unity and common prosperity of all ethnic groups.
– The system of regional ethnic autonomy has been fully implemented.
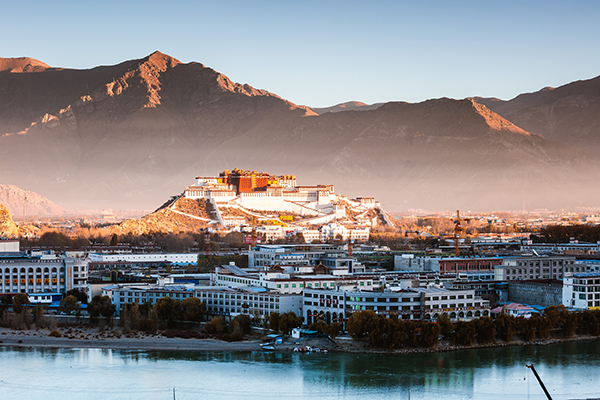
The system of regional ethnic autonomy is a basic political system of the state. In 1965, the Tibet Autonomous Region was founded and its People's Committee was elected. Since then, the system of regional ethnic autonomy has been fully implemented in Tibet. In 1984, the central government promulgated and implemented the Law on Regional Ethnic Autonomy of the People's Republic of China. After decades of experimentation and practical work, people of all ethnic groups in Tibet have built ethnic relationships characterized by equality, unity, mutual support and harmony.
People in Tibet enjoy the right to be masters of the country and the region in accordance with the law. Since its founding, the autonomous region has issued 152 local regulations and normative documents, providing an important legal guarantee for the rights and interests of all ethnic groups. People in Tibet actively exercise the right to vote and stand for election as prescribed by the Constitution and laws; they participate in the election of deputies to people's congresses at the national and local levels, and in the administration of state and local affairs. Since 1979, elections have been held at the regional, prefectural (city), county and township (town) levels, with the voter participation rate above 90 percent, and in some places as high as 100 percent. Of the 439 deputies to the 11th People's Congress of the Tibet Autonomous Region announced on January 18, 2018, 289 – almost exactly two-thirds – are from the Tibetan and other ethnic minorities. Most of the current and previous members of the Tibetan Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference are or were Tibetan and other ethnic minorities. The state supports equal participation and joint management by all ethnic groups, and sets up ethnic townships in areas where ethnic groups with small populations live in compact communities, to protect the rights and interests of these groups. At present, nine ethnic townships have been set up in Shannan, Nyingchi and Qamdo, of which five are Monba townships, three are Lhoba townships and one is a Naxi township.
The state pays great attention to the training of officials and personnel from minority ethnic groups. After the liberation of Tibet, especially during democratic reform, a large number of liberated serfs and slaves grew rapidly into outstanding officials. By setting up a special institution to train and educate ethnic minority officials in 1981, and a leading group for official education in 1989, Tibet has cultivated a large number of administrative and technical ethnic minority officials through training, job rotation, providing work opportunities at the grass-roots, and arranging for leading officials to hold posts in different localities.
– The sense of national identity has been heightened.
Tibet has had a fine tradition of exchanges, communication, and integration among ethnic groups since ancient times. In the early 1950s, a large number of people from various ethnic groups and sectors in Tibet visited other parts of China. Since reform and opening up in 1978, economic and cultural exchanges between ethnic groups have become closer and the sense of national identity has grown stronger. Every year on National Day, and during the Peaceful Liberation Celebration and the Ethnic Unity Month, Tibet conducts themed education on the Chinese Dream and patriotism. Thanks to these efforts, ethnic unity and progress have been promoted. To date the State Council and the Tibet Autonomous Region have presented 1,985 awards to exemplary organizations and 2,846 awards to exemplary individuals for ethnic unity and progress. Lhasa, Xigaze, Qamdo and Ngari have each become demonstration cities (prefectures) for ethnic unity and progress. By the end of 2020, Tibet had promulgated and implemented one regulation – Regulations on the Establishment of Model Areas for Ethnic Unity and Progress – and four normative documents on ethnic unity and progress. Tibetan students and workers are free to find jobs and start businesses anywhere in the rest of China. Every year, more than 10 percent of Tibetan college students take jobs outside the autonomous region.
The autonomous region encourages people from other parts of China to study, invest and start businesses in Tibet, and constantly creates innovative new measures to attract investment. Since 2016, the region has issued 52 special preferential policies related to taxation, finance, and land, which have effectively improved the efficiency of administrative examination and approval and the quality of services. As a result, a total of RMB253.5 billion has been in place. The region has also worked hard to create an integrated social structure and community environment for all ethnic groups, promote equal access to public services, protect the legitimate rights and interests of ethnic minorities living in cities and scattered residential areas, and respect their festive, food and funeral customs and traditions.
– Freedom of religious belief is fully protected.
In Tibet, all religions and sects are equal, as are all believers and non-believers. There are more than 1,700 sites for Tibetan Buddhist activities with 46,000 monks and nuns, 4 mosques serving 12,000 native Muslims, and a Catholic church with more than 700 followers. In order to adapt religions to the Chinese context, ensure the freedom and order of religious belief, and manage religious affairs in accordance with the law, the state has formulated the Measures on the Management of the Reincarnation of Living Buddhas of Tibetan Buddhism in accordance with the Regulations on Religious Affairs. It has also formulated a series of policies, measures and regulatory documents, which include Measures of the Tibet Autonomous Region on Implementing the Regulations on Religious Affairs (trial), Measures of the Tibet Autonomous Region on the Management of Major Religious Activities, and Detailed Rules of the Tibet Autonomous Region for the Implementation of the Measures on the Management of Living Buddha Reincarnation of Tibetan Buddhism.
The reincarnation of Living Buddhas has been carried out in an orderly manner in accordance with laws, regulations, religious rituals and historical conventions. In 1995, with the approval of the State Council, the search for and identification of the reincarnation of the 10th Panchen Lama and the enthronement of the 11th Panchen Lama were completed by drawing lots from a golden urn. In 2010, the Sixth Living Buddha Dezhub was identified and enthroned through the drawing of lots from a golden urn and with the approval of the government of the Tibet Autonomous Region. By 2020, 92 reincarnated Living Buddhas had been identified and approved through traditional religious rituals and historical conventions. Traditional religious activities are carried out regularly in accordance with the law – activities such as studying scriptures and debate, initiation as a monk or nun, abhisheka (an empowerment ceremony), and self-cultivation. Examination on scriptures and subsequent promotion in academic degrees are also held in monasteries on a regular basis.
The Tibetan Buddhist Institute and its 10 branches now have more than 3,000 monks and nuns who are studying the sutras, and 240 received senior academic titles between 2005 and 2020. Monastery-run scripture printing houses have been conserved and developed; there are three large-scale printing houses at the Potala Palace and other monasteries. Religious believers regularly participate in various religious and traditional activities such as the Saga Dawa Festival, the Monlam Prayer Festival in Lhasa, the Tour of Gangdise Mountains in the Year of the Horse, and the Tour of Lake Namtso in the Year of the Sheep. Currently more than 600 religious figures serve as deputies or members of people's congresses and political consultative conferences at various levels.








