Lhasa
Updated: 2022-12-16 (chinadaily.com.cn)  Print
Print 

(1) Historical geography
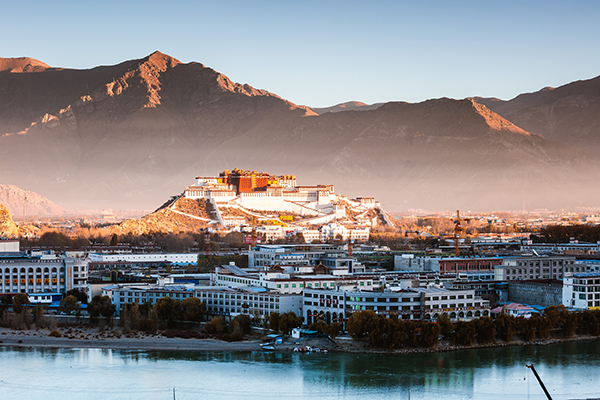
Lhasa, known as Luoxie in ancient times, is a famous historical and cultural city in China. In the 7th century, the Tibetan king, Songtsengampo, unified the entire region and moved the political center from Lhokha to Lhasa. After 1,000 years of development, it became the political, economic, cultural, and religious center of Tibet.
Tibet was peacefully liberated in 1951, and, in January 1960, Lhasa was established. In September 1965, the Tibet autonomous region was established, and Lhasa became the capital of the autonomous region.
Lhasa is located in central and southern Tibet. It is approximately 277 kilometers long from east to west, and stretches about 202 kilometers from north to south. It is connected to Nyingchi city to the east, Shigatse city to the west, Lhokha city to the south, and Nagchu city to the north.
It covers an area of 29,640 square kilometers, is 3,658 meters above sea level, and experiences more than 3,000 hours of sunshine per year. It is known as the "Sunlight City" and is part of the first batch of 24 historical and cultural cities announced by the State Council.
The city has two national nature reserves and two national forest parks. There are 389 key cultural relics protection units, of which 18 are national key cultural relic protection units, including one world cultural heritage. It is also home to 108 region-level key cultural relic protection units, 54 municipal-level key cultural relic protection units, and 209 county-level key cultural relic protection units.
(2) Population division
By the end of 2019, the registered population of Lhasa was 558,900, an increase of 4,500 from the end of the previous year.
The city governs eight counties and districts, namely Chengguan district, Doilungdechen district, Dagze district, Lhundrub county, Damshung county, Nyemo county, Chushul county, and Maldrogungkar county, alongside the Lhasa National Economic and Technological Development Zone, Liuwu New District, the Innovation Park and Konggang New District. It is home to 37 townships, 12 towns, 16 sub-district offices, 50 communities, and 227 administrative villages.
(3) Economic and social development
In 2019, the city's gross regional product was 61.788 billion yuan, an increase of 8 percent year-on-year, of which the added value of the primary industry surpassed 2 billion yuan, an increase of 8.2 percent; the added value of the secondary industry was 23.61 billion yuan, an increase of 7.4 percent, and the added value of the tertiary industry was 36.16 billion yuan, an increase of 8.4 percent.
The per capita GDP was 86,750 yuan, a year-on-year increase of 5.5 percent. The general public budget revenue exceeded 11.7 billion yuan, an increase of 6.3 percent, and the fiscal self-sufficiency rate reached 42 percent.
There were 13,000 new jobs in cities and towns, and 171,000 re-employments of farmers and herdsmen, helping to further realize full employment.
It is estimated that the per capita disposable income of urban residents will exceed 40,000 yuan, and the per capita disposable income of farmers and herdsmen will reach 16,260 yuan, an increase of 12 percent and 13.2 percent respectively.
The income of farmers and herdsmen has doubled when compared with 2010, with the goals and tasks of the 13th Five-Year Plan (2016-20) have been completed ahead of schedule.
Basic public education, social insurance, medical and health care, social services, culture and sports and other public service development indicators, have all reached either the national or west-regional average level.








