Regulations on individual income tax for foreigners working in China
I. To determine whether a foreign individual working in China without a domicile is subject to Chinese tax, it is necessary to look at how long he or she has spent in China and where his or her employer is based in a tax year.
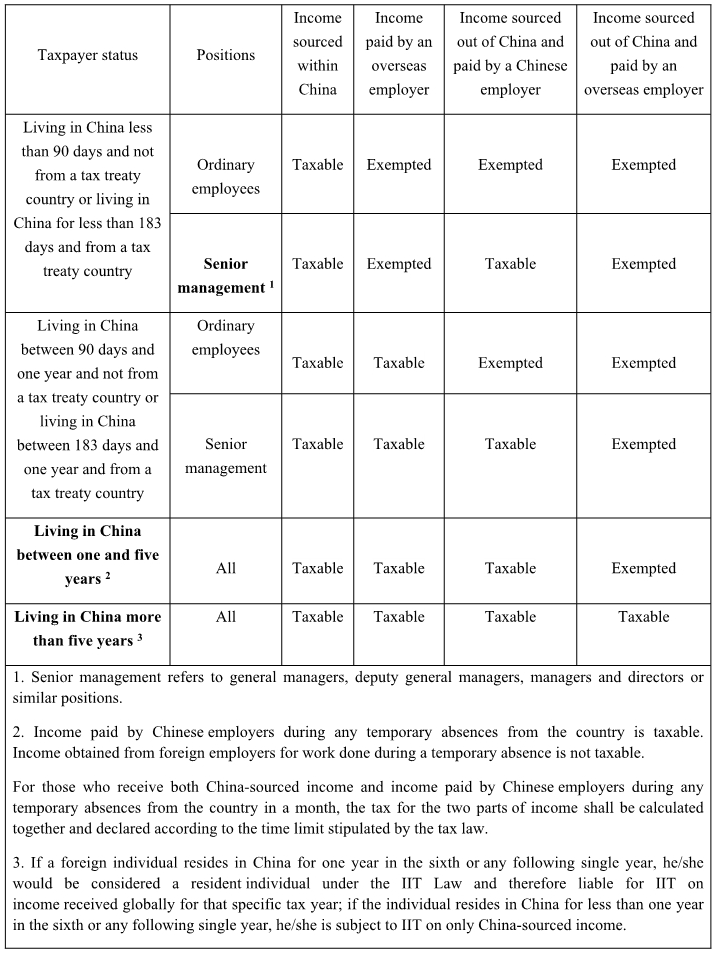
II. The calculation of IIT for income from wages and salaries
1. Income from wages and salaries includes wages, salary, bonuses, year-end bonuses, labor bonuses, allowances, subsidies and other income related to employment.
2. Monthly taxable income is calculated after a standard monthly deduction from the monthly income, that is:
monthly taxable income = monthly income - standard deduction.
3. Standard deduction:
According to the Individual Income Tax Law of the PRC and regulations, foreign individuals employed in China are eligible to a standard deduction of 4,800 yuan.
4. Income from wages and salaries, applying to a seven-level progressive tax rate, shall be taxed at rates ranging from 3 to 45 percent as follows:
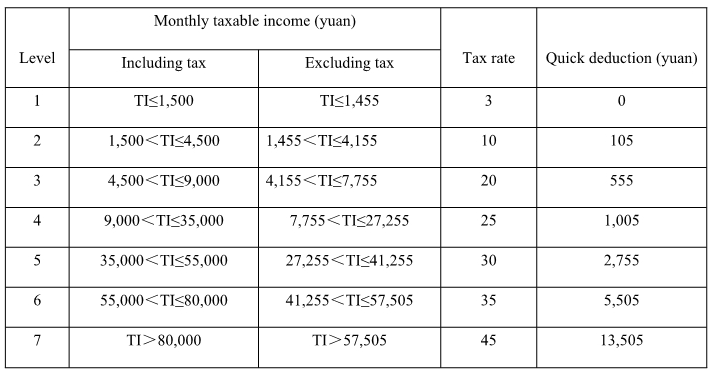
Note:
1. Both “Including tax” and “Excluding tax” in the above form refer to the amount of income after deduction of relevant expenses stipulated by the tax law.
2. “Including tax” applies to income from wages and salaries where the taxpayer bears the tax bill; while “excluding tax” applies to income from wages and salaries where others or the employer pay the tax.
3. Tax payable = Monthly taxable income × Applicable tax rate – Quick calculation deduction
III. Regulations on tax exemption
1. Regulations for the exemption of income from wages and salaries of foreign individuals
The income from wages and salaries of correspondents in China shall be taxable according to the regulations on IIT for foreigners working in China. If they require exemption, the procedures shall be handled through diplomatic channels on the principle of reciprocity, that is to say, only when their countries clearly stipulate that the ITT of Chinese correspondents can be exempted, can their IIT be exempted in China.
2. Exemption regulations for subsidies and allowances granted to foreign individuals
(1) Housing, food allowance and laundry fee:
Reasonable housing subsidies, food subsidies and laundry expenses of foreign individuals obtained by non-cash or on an actual reimbursement basis shall be exempted from individual income tax. The taxpayer should provide valid certificates to the competent tax authorities for examination and approval the first time he or she obtains the aforesaid subsidies or the month following any change to the amount or method of payment of the above subsidies.
(2) Relocation fee
Any relocation income a foreign individual acquires for working in or resigning from a position in China, paid by way of complete reimbursement, shall be exempted from personal income tax. The taxpayer shall provide valid certificates to the tax authorities in China for examination and approval.
(3) Travel allowance
Reasonable domestic and foreign travel allowance is exempt from individual income tax. The transportation fee, lodging fee certificate (copy) or business trip plan shall be provided by taxpayer and reviewed by the competent tax authorities to confirm the tax exemption.
(4) Visiting fee
Individual income tax shall be exempted for any family visit fees obtained by foreign individuals. The taxpayer should provide transportation expenditure vouchers for the family visit (copy), which shall be examined and approved by the competent tax authorities. Moreover, the preferential treatment of tax exemption only applies to the foreigner’s travelling between his or her employment places in China and the place of his or her family (including the residence of his or her spouses or parents) no more than twice a year.
(5) Language training fee and allowance for children's education
Individual income tax shall be exempted for language training fees and allowance for children's education received by foreign individuals. The taxpayer shall provide the vouchers and time limit documents for the acceptance of the above-mentioned education within the territory of China, which will be examined and approved by the competent tax authorities.
3. Regulations for the exemption of income from interest, dividends and bonuses of foreign individuals
(1) Income from interest, dividends and bonuses earned by foreign individuals from foreign-invested enterprises may be exempted from IIT. ( Notices on Some Policy Issues on Personal Income Tax released by the Ministry of Finance and State Administration of Taxation Document: Caishuizi No 0202[1994])
(2) Dividends (bonuses) received by foreign individuals holding B-shares or overseas shares (including H-shares) from China-based enterprises which issued such shares are temporarily exempted from individual income tax. (Letter of the SAT on Taxation Issues regarding Dividends Received by Foreign Individuals Holding Shares of China-based Listed Companies Document: Guoshuihanfa No 440 [1994]).
IV. Regulations on tax collection
1. Registration information of foreign individuals
Foreign personnel shall receive the Personal Income Tax Registration Form (two copies) and the Monthly Declaration Form of Personal Income Tax (two copies) from the foreign individual registration window of the local tax bureau within three months from the first date of their first arrival in China, and then take the following certificates and documents to the window for foreign personal registration after completion:
(1) Personal Income Tax Registration Form and the Monthly Declaration Form of Personal Income Tax;
(2) The wage and salary certificates issued by the headquarters of the employer that indicate whether the taxpayer has any part-time job in or outside the country and the details about the income, with details about when the income was obtained and the payer of the personal income tax.
(3) A certificate of appointment (copy) approved by the related ministries and commissions and the employment contract signed with the company (copy).
(4) Passport, the Mainland Travel Permit for Hong Kong and Macao Residents or the Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents (Full copy including the blank pages)
(5) Resident permit (Full copy).
2. Registration cancellation of foreign individuals
A foreign individual who leaves the office shall submit the registration cancellation with the following relevant materials to the local tax bureau’s branch office of the place of residence within thirty days from the date of tax payment:
(1) Employment separation certificate issued by the headquarter of the employer;
(2) Photocopy of tax payment book of the year of leaving post and the previous year;
(3) A full copy of the passport (including blank pages) of those foreign individuals who have a position overseas and pay tax on a daily basis;
(4) Copy of the passport or air ticket of those foreign individuals who pay tax on a daily basis in the month of leaving the position.
The tax authorities shall review the documents within 15 working days.
3. Personal income tax declaration
Foreign individuals shall declare their personal income tax of the previous month at the tax bureau’s branch that handles foreign affairs in the place of residence in the first seven days of the following month. If the last day of the first seven days is a legal holiday, the next day after the holiday will be the last day of the deadline; if there are more than three consecutive days of legal holiday during the period of time, the deadline is postponed according to the holiday days. The tax authorities will examine and review the materials within 15 working days.
